개발/JAVA
예외처리-JAVA
도비의 양말을 찾아서
2023. 2. 6. 20:33
1. 예외의 계층 구조
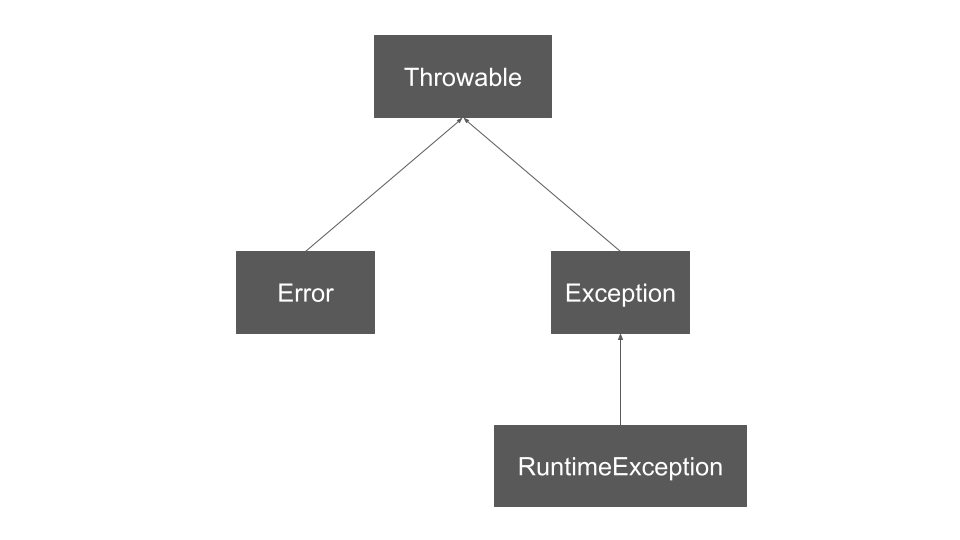
- 객체를 예외로 전달하기 위해 Throwable형으로 되어 있다.
- Error의 경우 시스템이 종료되어야 할 수준의 심각한 문제. (ex. OutOfMemoryError)
- Excepthon의 경우 로직에서 발생한 실수.(ex.IllegalArgumentException)
- RuntimeException : 실행시 발생
- Exception : 컴파일시 발생
2. 예외 예시
- try-catch
package org.example;
public class Sample {
public void finallyPrint() {
System.out.println("ok thanks.");
}
public void exceptionPrint() {
System.out.println("excpetion.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample sample = new Sample();
int c;
try {
c = 4 / 0;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
c = -1;
sample.exceptionPrint();
}
}
}- try-catch-finally
package org.example;
public class Sample {
public void finallyPrint() {
System.out.println("ok thanks.");
}
public void exceptionPrint() {
System.out.println("excpetion.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample sample = new Sample();
int c;
try {
c = 4 / 0;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
c = -1;
sample.exceptionPrint();
}
finally {
sample.finallyPrint(); // 예외에 상관없이 무조건 수행.
}
}
}
3. 사용자 정의 예외
- Exception을 상속 받음.
- throw를 통해 예외를 강제로 발생
package org.example;
class FoolException extends Exception {
}
public class Sample {
public void sayNick(String nick) throws FoolException {
if("fool".equals(nick)) {
throw new FoolException();
}
System.out.println("당신의 별명은 "+nick+" 입니다.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample sample = new Sample();
try {
sample.sayNick("fool");
sample.sayNick("genious");
} catch (FoolException e) {
System.err.println("FoolException이 발생했습니다.");
}
}
}